There are three main manufacturers of graphics cards.
- Intel HD
- AMD Radeon HD
- NVIDIA GeForce
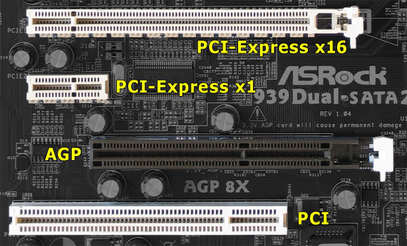
The CPU's motherboard will have a plug-in for the graphics card. These plug-ins can vary in size depending on the CPU. The plug-in sizes are generally PCI Express 2.0x16 or PCI Express 3.0x16. A 2.0 vs 3.0 plug-in doesn't generally matter for the graphics card. A 2.0 graphics card can plug into a 3.0 motherboard plug-in and vice versa with little to no performance loss. The problem comes into play when a CPU has a x8 plug-in rather than a x16 plug-in. This type of plug-in is only found in older CPU's and will see a noticeable performance loss from a graphics card that has x16.
A graphics card's maximum resolution is the highest resolution the graphics card can achieve. It is important to note that the maximum resolution is not the resolution the computer will display, it is the maximum the card can support. In order to actually achieve maximum resolution, the correct plug-in on the graphics card must be used. Graphics cards have several different plug-ins allowing different resolutions. To get maximum resolution the port allowing the maximum resolution must be plugged-in and the display unit being used must also be able to support the maximum resolution.
Core Speed is the operation speed of the graphics card. This speed is measured in MHz or GHz (frequency). The overall speed of the graphics card is not solely determined by the core speed. The memory speed and size must also be taken into account. If it is assumed that the the graphics cards are identical except for the core speed, the faster core speed will determine the faster card.
The only downside to having a higher core speed is that it requires more energy and therefor produces more heat. This requires more cooling in the CPU with either fans or liquid cooling.
A newer feature found on graphics cards is called a speed boost. This new feature allows allows the graphics card to temporarily increase its performance speed when the program being used requires more graphics output. The speed boost is only able to occur if the graphics card is under a certain power and temperature threshold.
The only downside to having a higher core speed is that it requires more energy and therefor produces more heat. This requires more cooling in the CPU with either fans or liquid cooling.
A newer feature found on graphics cards is called a speed boost. This new feature allows allows the graphics card to temporarily increase its performance speed when the program being used requires more graphics output. The speed boost is only able to occur if the graphics card is under a certain power and temperature threshold.
The stream processor is the amount of cores the GPU has. The more cores a GPU has the faster it can perform tasks and create graphics. More stream processors yields better performance. There is no downside to have more stream processors.
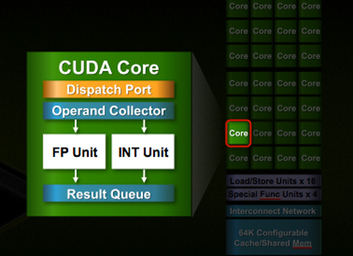
An important note is that you can't compare stream processor of differing graphics cards. A GPU that has 2048 stream processors could yield the same processing speed as a GPU with 1344 stream processors. This is because different manufacturers have created different cores. For example NVIDIA uses CUDA cores. These cores on a single level are faster than other cores, so even with less cores, 1344 stream processors, the graphics card can have the same processing speed as a card with 2048 stream processors.
An important note is that you can't compare stream processor of differing graphics cards. A GPU that has 2048 stream processors could yield the same processing speed as a GPU with 1344 stream processors. This is because different manufacturers have created different cores. For example NVIDIA uses CUDA cores. These cores on a single level are faster than other cores, so even with less cores, 1344 stream processors, the graphics card can have the same processing speed as a card with 2048 stream processors.
A graphics card's video memory is the card's RAM that is separate from the CPU's RAM. This is the amount of temporary data storage space the card has. More RAM is generally better to have, but having more RAM than a program can use will yield no greater performance.
Memory speed (also measured in MHz, same as core speed) is the speed at which the graphics card is able to access the memory. The better the memory speed, the faster the memory can be accessed and the faster processes can be carried out.
Memory bus width determines the amount of memory the graphics card can access per each clock cycle. The wider the bus width, the more memory can be accessed per cycle, the faster the card can perform processes.
Bandwidth is basically the overall speed of the graphics card. Bandwidth is calculated using memory speed and size along with core speed and stream processors to give an overall idea of how fast the graphics card can actually perform.
Memory speed (also measured in MHz, same as core speed) is the speed at which the graphics card is able to access the memory. The better the memory speed, the faster the memory can be accessed and the faster processes can be carried out.
Memory bus width determines the amount of memory the graphics card can access per each clock cycle. The wider the bus width, the more memory can be accessed per cycle, the faster the card can perform processes.
Bandwidth is basically the overall speed of the graphics card. Bandwidth is calculated using memory speed and size along with core speed and stream processors to give an overall idea of how fast the graphics card can actually perform.
https://www.pugetsystems.com/labs/articles/Specs-Explained-Video-Card-463/